
from drivelinebaseball.com
Spin Rate: What We Know Now
This article is intended to build a basis of knowledge of what we, at Driveline Baseball, understand about spin rate at this current time. We will hopefully answer some common questions that we receive and well as link out to resources that we've found helpful in understanding spin rate. This article will also be a reference point for some of our further research and writing on spin rate.
Magnus Force and Spin Rate
We know that we can look at a group of pitchers throwing fastballs at the same speed, say 92 MPH, and those pitchers can all have different rates of spin on their fastballs. The rough guidelines for an 'average' pitcher would be a pitch at 92 MPH fastball with a spin rate of 2200 Revolutions per minute (RPM). In reality pitchers can throw 92 and have spin rates ranging from 1800 RPM to 2400 RPMs.
Why this happens can be explained by some simplified physics, in this case we'll focus on the Magnus force. If we picture a four seam fastball, which is thrown with backspin, the more backspin the less the ball is going to drop over its course from the pitcher's hand to the catcher's glove.
Here is a great gif illustrating this effect. This ball is traveling to the left with backspin, meaning the ball is pushing the air downward behind it creating an equal and opposite force upward. So you can see the faster the backspin the faster the air is deflected downwards and the higher the force pushing the ball back upward.
This gif was created from a fantastic video on the Magnus effect from Veritasium titled: What Is The Magnus Force?
So now let's think of the Magnus force in terms of spin rate.
A 92 MPH fastball at 2200 RPM is going to travel on an 'average' path to the plate.
If this 92 MPH fastball is thrown at 1800 RPM that means less spin, less Magnus force meaning the ball will drop further over its course to the plate than the 'average' fastball described above.
If this 92 MPH fastball is thrown at 2400 RPM that means more spin, more Magnus force meaning the ball will drop less over its course to the plate the the 'average' fastball.
These are small enough differences that a batter would not be able to tell before they decide to swing, but the balls will end up at different heights by the time they reach the plate.
What do high/low spin rates mean to a hitter?
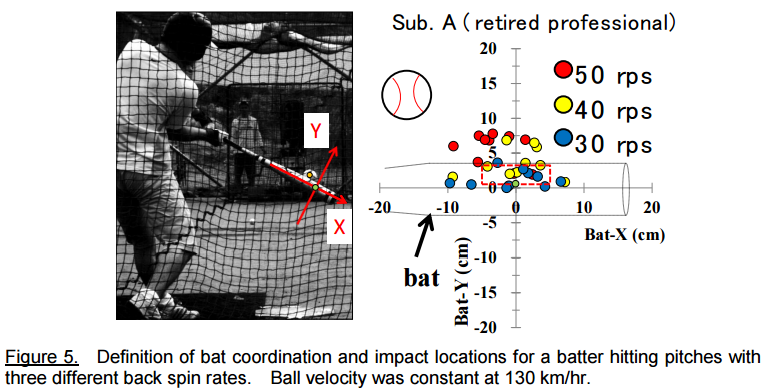
One study has examined how pitches with the same velocity but different spin rates would affect hitters.
This study used a pitching machine to throw pitches at 130 km/hr (80 MPH) at 50 RPS (Red 3000 RPM), 40 RPS (Yellow 2400 RPM), and 30 RPS (Blue 1800). You can see that even at the same speed hitters were consistently under the higher spin fastballs.
From: The Effect of Fastball Backspin Rate on Baseball Hitting Accuracy: Higuchi, et al.
Picture from: Baseball Spin and Pitchers' Performance: Kanosue, et al. (Open Access)
Now the highest spin fastball is spinning at faster than what we've seen in MLB pitchers, but the point still stands. Baseball is a game of millimeters when it comes to making or preventing good contact. So when you can throw fastballs with spin that are further away from average, the more beneficial it can be.
This would be in line with what Zach Day examined in 2013 finding that higher spin fastballs had more swing and misses and fewer ground balls. Lower spin fastballs the reverse, less swing and misses and more ground balls.
So we can say that at the same velocity the higher the spin rate the more swing and misses the fastball is going to get.
This chart from Jeff Zimmerman also supports this idea , finding that when looking at fastballs at the same velocity the higher the spin rate the higher the percentage of swinging strikes.
Jeff Long recently examined the correlations between spin rate and swinging strike%, GB%, and FB% and only found very small relationships with regards to spin when looking at all pitches. In this instance the effects of high and low spin rate most likely equaled themselves out.
Can you create higher or lower spin rate?
Higher spin – not necessarily. Lower spin – maybe.
With the knowledge that splitters have a noticeably lower spin rate than fastballs, we can assume that the splitter grip (where the index and middle fingers are very spread out on the ball) leads to a decrease in spin rate. Although we have not officially examined this theory, our preliminary testing agrees that an increased spacing between the fingers on the ball leads to a decrease in spin rate.
Beyond that, nobody truly knows how to reliably and consistently change the spin rate of pitchers. Mostly because no one knows why the ball spins differently from pitcher to pitcher.
What we do know if that there is good evidence that spin rate is created in an incredibly short amount of time.
From: Baseball Spin and Pitchers Performance: Kanosue et al. (Open Access)
Here the authors present picture evidence that suggests how quickly the ball goes from not rotating to rotating when a pitcher throws. Considering the acceleration phase of the throw lasts anywhere from 30-50 ms the suggestion that spin may be generated in only 6 ms(or just longer than that) of the motion is incredible. Each picture frame above is 6 ms long, you can see the ball goes from not rotating to rotating and being released in nearly one frame.
What is the relationship between spin rate and velocity?
We do have some evidence that spin rate is an innate characteristic, and is linearly related with velocity. We had 6 pitchers throw 20 pitches at velocities from 60-80 MPH. The pitchers were told to use the same fastball grip with the same mechanics and attempt to throw a fastball starting at 60 MPH followed by a pitch at 61 MPH all the way up to 80 MPH. The R^2 values between velocity and spin rate of the first 5 pitchers ranged from 0.83-0.96 which is quite a high relationship!
You can find the data here.
The 6th pitcher threw pitches from 60 – 80 MPH but was told to attempt to change his mechanics from pitch to pitch and you can see that the R^2 relationship dropped down to .541. Though this is merely a starting point for more research we can reasonably say that spin rate is an innate characteristic but unknown mechanical changes may also affect spin rate.
So this data suggests that we can say there is an innate relationship between spin rate and velocity for an individual pitcher but not across a large population of pitchers.
Meaning that if one pitcher could throw harder under the same mechanics and same grip his spin rate should increase. But his spin rate could 'max out' at 1900 at 92 MPH. While another pitcher may be able to throw harder under the same mechanics and same grip but his spin increase to 2400 at 92 MPH. This is obviously taking into considering a large assumption that they could throw harder with the same mechanics.
So pitchers may be able to increase their velocity and spin rate but we don't know where they will end up on the scale of 1800 – 2400 RPM for fastballs. Not every pitcher throwing 98+ has a ridiculous high spin rate. Just like not every pitcher throwing 90 has a low spin rate.
You can see this laid out further in this Statcast piece on velocity vs. spin rate.
What are Bauer Units?
In order to better compare spin rates at different velocities between pitchers we created Bauer Units (BU).
BU = Spin Rate (RPM)/Velocity (MPH)
This enables us to normalize the spin per the velocity of the pitch. If a pitcher is spinning a fastball at 2400 RPM, that is less impressive at 99 MPH and much more impressive at 89 MPH. Making spin rate more useful over a wide range of pitchers of varying velocities.
To more effectively compare Bauer Units of varying pitchers, we can normalized Bauer Units into a new unit, called BU+, which accounts for the league average Bauer Unit of pitchers.
BU+ = (Player BU/League Average BU)*100
This gives you an idea of how much high or lower a pitcher's spin is vs. Major League average, where a BU+ of 100 is perfectly average. A BU+ of greater than 100 would indicate a higher than average spin rate fastball, where as a BU+ of less than 100 would be a lower than average spin rate fastball.
Unfortunately, MLB and other statistic collecting agencies have yet to recognize our pioneering efforts into the field of baseball statistics.
This was also discussed on Statcast's 8/26/16 Podcast: The Art of Spin Rate
Are pitchers with higher spin rates more likely to be injured?
No, not that we can tell.
Though there is a growing belief that drastic changes in spin rate (usually sharp decreases) can be a sign of an injury or pending injury.
Each pitcher is going to have a small range around their average spin rate. Sharp changes from that normal range can be seen as an early sign of unhealthy fatigue. So teams can monitor their pitchers spin rate to see if there are any sustained drops of spin rate from their average. This would also work hand in hand with monitoring a pitcher's velocity.
Now this method of injury prevention hasn't been proven to be predictive over a large group of pitchers but it's simply another variable for teams to watch. Obviously at this time these types of analysis are only able to be done with MLB/MiLB pitchers.
This idea was also explained further in these Fangraphs pieces: A New Way to Study Pitching Injury and Pitcher Spin Rates and Injuries.
How can we use spin rate to our advantage?
For pitchers that come to our facility we can use either Trackman or Rapsodo to get measurements of their spin rates and then make recommendations on how to best use their pitchers or make tweaks to improve their pitches. In the case of fastballs, again we don't know how to change spin rate, but we can make recommendations on how to sequence pitches or location preferences.
An example would be a pitcher with a high spin fastball consistently being told to throw fastball at a hitters knees. In this case his fastballs aren't going to drop as much compared to the 'average' fastball meaning he might have a higher chance of getting hit being down in the zone. Pitching middle/up in the zone may be more beneficial in hopes of inducing pop-ups and swinging strikes.
The reverse is true for pitchers who have low spin fastballs. Staying down in the zone would be the best option because hitters should swing just over the pitch resulting in more ground balls. If someone if sitting right in the average range then we move on to looking at the other pitches he throws. Because we want pitches that are further away from the 'average' spin.
Hopefully this answers some basic questions on what we know about spin rate right now, we look forward to continuing our research with Trackman and Rapsodo.
This article was co-written by Assistant Researcher Michael O'Connell, Engineering Intern Joe Marsh and edited by Kyle Boddy
Sent from my iPhone


No comments:
Post a Comment